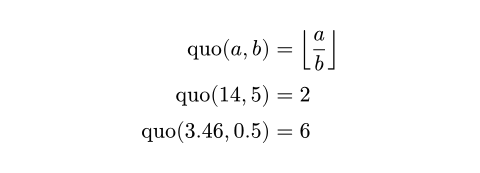このページは日本語に翻訳済みです。
Calculation
数値の計算と処理を行うためのモジュール。
これらの定義はcalcモジュールの一部であり、デフォルトではインポートされません。
以下に挙げる関数のほかに、calcモジュールは定数pi、tau、e、およびinf
を定義しています。
Function
abs
abs絶対値。
#calc.abs(-5) \
#calc.abs(5pt - 2cm) \
#calc.abs(2fr) \
#calc.abs(decimal("-342.440"))

calc.abs()->anypow
pow冪乗。
#calc.pow(2, 3) \
#calc.pow(decimal("2.5"), 2)

calc.pow(,)->exp
expeの冪乗。
#calc.exp(1)

calc.exp()->sqrt
sqrt平方根。
#calc.sqrt(16) \
#calc.sqrt(2.5)
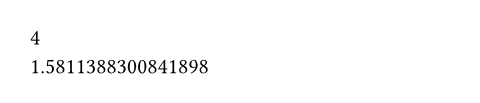
calc.sqrt()->root
rootn乗根。
負の値の場合、nは奇数でなければなりません。
#calc.root(16.0, 4) \
#calc.root(27.0, 3)

calc.root(,)->sin
sinサイン(正弦)の計算。
整数または浮動小数点数で呼び出された場合、それらはラジアンとして解釈されます。
#calc.sin(1.5) \
#calc.sin(90deg)

calc.sin()->cos
cosコサイン(余弦)の計算。
整数または浮動小数点数で呼び出された場合、それらはラジアンとして解釈されます。
#calc.cos(1.5) \
#calc.cos(90deg)

calc.cos()->tan
tanタンジェント(正接)の計算。
整数または浮動小数点数に対して呼び出された場合、それらはラジアンとして解釈されます。
#calc.tan(1.5) \
#calc.tan(90deg)

calc.tan()->asin
asinアークサイン(逆正弦)の計算。
#calc.asin(0) \
#calc.asin(1)

calc.asin()->acos
acosアークコサイン(逆余弦)の計算。
#calc.acos(0) \
#calc.acos(1)

calc.acos()->atan
atanアークタンジェント(逆正接)の計算。
#calc.atan(0) \
#calc.atan(1)

calc.atan()->atan2
atan2四象限アークタンジェントの計算。
引数の順序は(y, x)ではなく(x, y)です。
#calc.atan2(1, 1) \
#calc.atan2(-2, -3)

calc.atan2(,)->sinh
sinhハイパーボリックサイン(双曲線正弦)を計算。
#calc.sinh(0) \
#calc.sinh(1.5)

calc.sinh()->value
valueハイパーボリックサインを計算する双曲角。
cosh
coshハイパーボリックコサイン(双曲線余弦)を計算。
#calc.cosh(0) \
#calc.cosh(1.5)
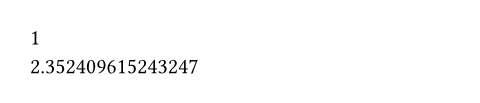
calc.cosh()->value
valueハイパーボリックコサインを計算する双曲角。
tanh
tanhハイパーボリックタンジェント(双曲線正接)を計算。
#calc.tanh(0) \
#calc.tanh(1.5)

calc.tanh()->value
valueハイパーボリックタンジェントを計算する双曲角。
ln
ln数値の自然対数。
#calc.ln(calc.e)

calc.ln()->fact
fact数値の階乗。
#calc.fact(5)

calc.fact()->number
number階乗を計算する数値。0または正の値である必要があります。
perm
perm順列の計算。
順列、つまり、n個の項目からk個を、順序を区別して選択する組み合わせの数を返します。
$ "perm"(n, k) &= n!/((n - k)!) \
"perm"(5, 3) &= #calc.perm(5, 3) $
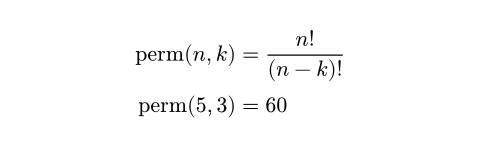
calc.perm(,)->binom
binom二項係数の計算。
n個の項目からk個を順序を区別せず選択する組み合わせの数を返します。
#calc.binom(10, 5)

calc.binom(,)->gcd
gcd2つの整数値の最大公約数。
#calc.gcd(7, 42)

calc.gcd(,)->lcm
lcm2つの整数値の最小公倍数。
#calc.lcm(96, 13)

calc.lcm(,)->floor
floor数値を最も近い整数値に切り捨て。
もしその値がすでに整数であれば、そのまま返されます。
この関数は常に整数値を返し、結果となるfloatやdecimalが64ビット符号付き整数の最大値より大きい、または最小値より小さい場合はエラーとなります。
#calc.floor(500.1)
#assert(calc.floor(3) == 3)
#assert(calc.floor(3.14) == 3)
#assert(calc.floor(decimal("-3.14")) == -4)

calc.floor()->ceil
ceil数値を最も近い整数値に切り上げ。
もしその値がすでに整数であれば、そのまま返されます。
この関数は常に整数値を返し、結果となるfloatやdecimalが64ビット符号付き整数の最大値より大きい、または最小値より小さい場合はエラーとなります。
#calc.ceil(500.1)
#assert(calc.ceil(3) == 3)
#assert(calc.ceil(3.14) == 4)
#assert(calc.ceil(decimal("-3.14")) == -3)

calc.ceil()->trunc
trunc数値の整数部分を切り出し。
もしその値がすでに整数であれば、そのまま返されます。
この関数は常に整数値を返し、結果となるfloatやdecimalが64ビット符号付き整数の最大値より大きい、または最小値より小さい場合はエラーとなります。
#calc.trunc(15.9)
#assert(calc.trunc(3) == 3)
#assert(calc.trunc(-3.7) == -3)
#assert(calc.trunc(decimal("8493.12949582390")) == 8493)

calc.trunc()->fract
fract数値の小数部分を切り出し。
もしその値が整数であれば、0を返します。
#calc.fract(-3.1)
#assert(calc.fract(3) == 0)
#assert(calc.fract(decimal("234.23949211")) == decimal("0.23949211"))
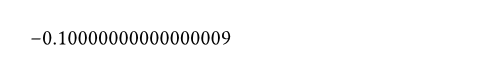
calc.fract()->round
round数値を四捨五入します。
オプションで、小数点以下の桁数を指定することも可能です。
指定する桁数が負の値の場合、その絶対値が小数点より左側で切り捨てる有効整数桁数を示します。
この関数は、演算対象と同じ型の値を返します。つまり、floatにroundを適用するとfloatが、decimalに適用するとdecimalが返されます。
関数の出力を明示的にintにすることも可能ですが、そのfloatやdecimalが64ビット符号付き整数の最大値より大きい場合、または最小値より小さい場合はエラーとなることに注意してください。
さらに、この関数は、整数やdecimalの最大値または最小値を超えて丸めようとするとエラーになる場合があります。数値がfloatの場合、そのような試みは、最大値や最小値に対してそれぞれfloat.infと-float.infを返します。
#calc.round(3.1415, digits: 2)
#assert(calc.round(3) == 3)
#assert(calc.round(3.14) == 3)
#assert(calc.round(3.5) == 4.0)
#assert(calc.round(3333.45, digits: -2) == 3300.0)
#assert(calc.round(-48953.45, digits: -3) == -49000.0)
#assert(calc.round(3333, digits: -2) == 3300)
#assert(calc.round(-48953, digits: -3) == -49000)
#assert(calc.round(decimal("-6.5")) == decimal("-7"))
#assert(calc.round(decimal("7.123456789"), digits: 6) == decimal("7.123457"))
#assert(calc.round(decimal("3333.45"), digits: -2) == decimal("3300"))
#assert(calc.round(decimal("-48953.45"), digits: -3) == decimal("-49000"))

calc.round(,)->clamp
clamp数値を最小値と最大値の間にクランプ。
#calc.clamp(5, 0, 4)
#assert(calc.clamp(5, 0, 10) == 5)
#assert(calc.clamp(5, 6, 10) == 6)
#assert(calc.clamp(decimal("5.45"), 2, decimal("45.9")) == decimal("5.45"))
#assert(calc.clamp(decimal("5.45"), decimal("6.75"), 12) == decimal("6.75"))

calc.clamp(,,)->クランプする数値。
最小値(この値を含む)。
min
min一連の値の最小値を決定。
#calc.min(1, -3, -5, 20, 3, 6) \
#calc.min("typst", "is", "cool")

calc.min(any)->anyvaluesany必須引数必須引数必須引数は、関数を呼び出す際に必ず指定しなければなりません。位置引数位置引数位置引数は順序通りに指定することで、引数名を省略して設定できます。可変長引数可変長引数可変長引数は複数回指定することができます。
values最小値を抽出する一連の値。空であってはなりません。
max
max一連の値の最大値を決定。
#calc.max(1, -3, -5, 20, 3, 6) \
#calc.max("typst", "is", "cool")

calc.max(any)->anyvaluesany必須引数必須引数必須引数は、関数を呼び出す際に必ず指定しなければなりません。位置引数位置引数位置引数は順序通りに指定することで、引数名を省略して設定できます。可変長引数可変長引数可変長引数は複数回指定することができます。
values最大値を抽出する一連の値。空であってはなりません。
even
even整数値が偶数かどうかを判定。
#calc.even(4) \
#calc.even(5) \
#range(10).filter(calc.even)

calc.even()->value
value偶数かどうかをチェックする数値。
odd
odd整数値が奇数かどうかを判断。
#calc.odd(4) \
#calc.odd(5) \
#range(10).filter(calc.odd)
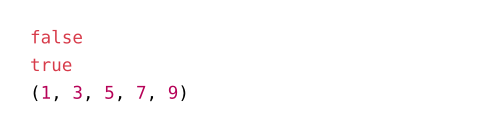
calc.odd()->value
value奇数かどうかをチェックする数値。
rem
rem2つの数値の剰余を計算。
calc.rem(x, y)の値は常にxと同じ符号を持ち、yよりも小さい絶対値になります。
decimalが入力され、被除数が除数に比べて絶対値が小さすぎる場合はエラーになることがあります。
#calc.rem(7, 3) \
#calc.rem(7, -3) \
#calc.rem(-7, 3) \
#calc.rem(-7, -3) \
#calc.rem(1.75, 0.5)

calc.rem(,)->div-euclid
div-euclid2つの数値のユークリッド除算を実行。
この計算の結果は、商を被除数が除数のn倍以上になる整数nに丸めた値です。
#calc.div-euclid(7, 3) \
#calc.div-euclid(7, -3) \
#calc.div-euclid(-7, 3) \
#calc.div-euclid(-7, -3) \
#calc.div-euclid(1.75, 0.5) \
#calc.div-euclid(decimal("1.75"), decimal("0.5"))

calc.div-euclid(,)->rem-euclid
rem-euclid除算の最小の非負剰余を計算。
警告:浮動小数点数の丸め誤差により、被除数が除数よりも極端に小さく、かつ負の値である場合、剰余が除数の絶対値と等しくなる可能性があります。 これは浮動小数点数の入力にのみ当てはまります。
また、decimalを入力した場合、被除数が除数に比べて桁違いに小さい場合はエラーとなることがあります。
#calc.rem-euclid(7, 3) \
#calc.rem-euclid(7, -3) \
#calc.rem-euclid(-7, 3) \
#calc.rem-euclid(-7, -3) \
#calc.rem-euclid(1.75, 0.5) \
#calc.rem-euclid(decimal("1.75"), decimal("0.5"))

calc.rem-euclid(,)->