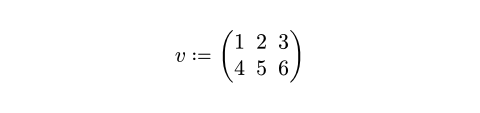翻訳済み
このページは日本語に翻訳済みです。
mat要素関数要素関数要素関数はsetルールやshowルールでカスタマイズできます。
要素関数
要素関数は
setルールやshowルールでカスタマイズできます。行列。
行内の要素はカンマで区切り、行自身はセミコロンで区切らなければなりません。 セミコロン構文は、直前にあるカンマ区切りの引数を配列にマージします。 数式関数呼び出しに関するこの特殊な構文は、2次元データを引数に取るカスタム関数の定義にも使用できます。
セル内のコンテンツはalignパラメーターを用いて配置できます。 また、同じ行にあるコンテンツは&記号を用いて配置できます。
例
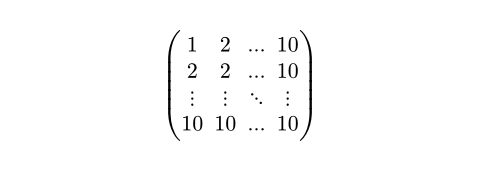
$ mat(
1, 2, ..., 10;
2, 2, ..., 10;
dots.v, dots.v, dots.down, dots.v;
10, 10, ..., 10;
) $
引数引数引数は関数への入力値です。関数名の後に括弧で囲んで指定します。
引数
引数は関数への入力値です。関数名の後に括弧で囲んで指定します。
math.mat(,,,gap:,,,)->用いる区切り文字。
単一の文字で左区切り文字を指定する場合、右区切り文字は自動的に推論されます。 それ以外の場合は、左区切り文字と右区切り文字を含む配列を指定します。
例を表示
#set math.mat(delim: "[")
$ mat(1, 2; 3, 4) $
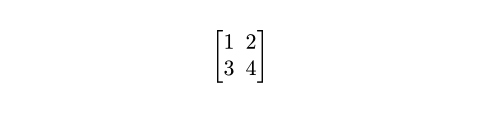
デフォルト値:("(", ")")
align設定可能引数設定可能引数設定可能引数は、setルールを用いて設定でき、それ以降で使用するデフォルト値を変更できます。
align設定可能引数
設定可能引数
設定可能引数は、
setルールを用いて設定でき、それ以降で使用するデフォルト値を変更できます。各セルの水平方向の配置。
例を表示
#set math.mat(align: right)
$ mat(-1, 1, 1; 1, -1, 1; 1, 1, -1) $
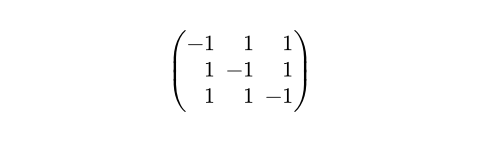
デフォルト値:center
augment設定可能引数設定可能引数設定可能引数は、setルールを用いて設定でき、それ以降で使用するデフォルト値を変更できます。
augment設定可能引数
設定可能引数
設定可能引数は、
setルールを用いて設定でき、それ以降で使用するデフォルト値を変更できます。行列内に補助線を描画。
none: 線は描画されません。- 単一の数値: 指定された列番号の後に垂直方向の線を描画します。 負数の場合は最後の列から数え始めます。
- 辞書: 水平方向および垂直方向の両方で複数の補助線を描画できます。
加えて線のスタイルを設定可能です。
辞書には以下のキーを含めることができます。
hline: 水平方向の線を描画するオフセット。 例えば、オフセットを2とすると行列の2行目の後に水平方向の線が描かれます。 単一の線を描く場合は整数を、複数の線の場合は整数の配列を受け取ります。 単一の数値を指定する場合と同様に、負数の場合は末尾から数え始めます。vline: 垂直方向の線を描画するオフセット。 例えば、オフセットを2とすると行列の2列目の後に垂直方向の線が描かれます。 単一の線を描く場合は整数を、複数の線の場合は整数の配列を受け取ります。 単一の数値を指定する場合と同様に、負数の場合は末尾から数え始めます。stroke: 線のストローク。autoが指定された場合、0.05emの太さで四角い線端になります。
例を表示:Basic usage
$ mat(1, 0, 1; 0, 1, 2; augment: #2) $
// Equivalent to:
$ mat(1, 0, 1; 0, 1, 2; augment: #(-1)) $
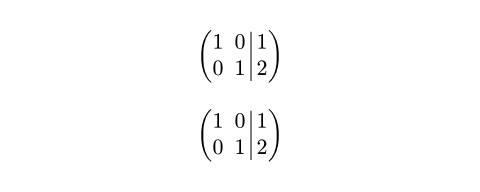
例を表示:Customizing the augmentation line
$ mat(0, 0, 0; 1, 1, 1; augment: #(hline: 1, stroke: 2pt + green)) $

デフォルト値:none
gap
gap行間と列間の間隔。
これはrow-gapとcolumn-gapを同じ値で設定する省略記法です。
例を表示
#set math.mat(gap: 1em)
$ mat(1, 2; 3, 4) $
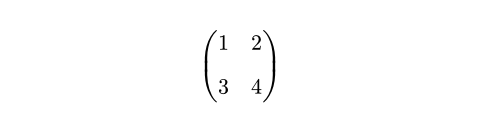
デフォルト値:0% + 0pt
row-gap設定可能引数設定可能引数設定可能引数は、setルールを用いて設定でき、それ以降で使用するデフォルト値を変更できます。
row-gap設定可能引数
設定可能引数
設定可能引数は、
setルールを用いて設定でき、それ以降で使用するデフォルト値を変更できます。行間の間隔。
例を表示
#set math.mat(row-gap: 1em)
$ mat(1, 2; 3, 4) $
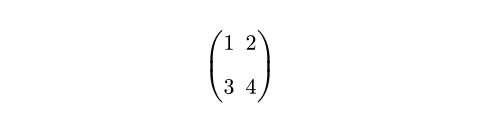
デフォルト値:0% + 0.2em
column-gap設定可能引数設定可能引数設定可能引数は、setルールを用いて設定でき、それ以降で使用するデフォルト値を変更できます。
column-gap設定可能引数
設定可能引数
設定可能引数は、
setルールを用いて設定でき、それ以降で使用するデフォルト値を変更できます。列間の間隔。
例を表示
#set math.mat(column-gap: 1em)
$ mat(1, 2; 3, 4) $
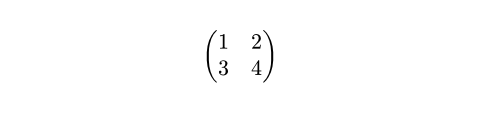
デフォルト値:0% + 0.5em
rows必須引数必須引数必須引数は、関数を呼び出す際に必ず指定しなければなりません。位置引数位置引数位置引数は順序通りに指定することで、引数名を省略して設定できます。可変長引数可変長引数可変長引数は複数回指定することができます。
rows必須引数
必須引数
必須引数は、関数を呼び出す際に必ず指定しなければなりません。
位置引数
位置引数
位置引数は順序通りに指定することで、引数名を省略して設定できます。
可変長引数
可変長引数
可変長引数は複数回指定することができます。
行列の各行を要素とする配列の配列。
例を表示
#let data = ((1, 2, 3), (4, 5, 6))
#let matrix = math.mat(..data)
$ v := matrix $