翻訳済み
このページは日本語に翻訳済みです。
arguments
関数に渡された引数。
引数シンク
組み込み関数と同様に、カスタム関数も可変長引数を受け取れます。
余分にある引数を全てまとめて受け取る引数シンク(キッチンシンクのようにさまざまなものが流れ込む先)は、..sinkの形で指定できます。このとき生成されるsinkの値はarguments型になります。この型は、位置引数と名前付き引数の両方にアクセスするためのメソッドを提供しています。
#let format(title, ..authors) = {
let by = authors
.pos()
.join(", ", last: " and ")
[*#title* \ _Written by #by;_]
}
#format("ArtosFlow", "Jane", "Joe")
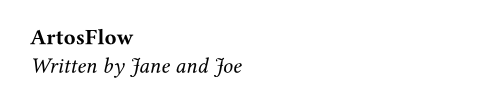
引数の展開
引数シンクとは逆に、..spread演算子を使うと、関数呼び出しにおいて引数や配列、辞書を展開して渡すことができます。
#let array = (2, 3, 5)
#calc.min(..array)
#let dict = (fill: blue)
#text(..dict)[Hello]

コンストラクタ引数引数は関数への入力値です。関数名の後に括弧で囲んで指定します。
引数
引数は関数への入力値です。関数名の後に括弧で囲んで指定します。
展開可能な引数をその場で生成します。
この関数は、let args(..sink) = sinkのように動作します。
#let args = arguments(stroke: red, inset: 1em, [Body])
#box(..args)

arguments(any)->argumentsany必須引数必須引数必須引数は、関数を呼び出す際に必ず指定しなければなりません。位置引数位置引数位置引数は順序通りに指定することで、引数名を省略して設定できます。可変長引数可変長引数可変長引数は複数回指定することができます。
argumentsany
必須引数
必須引数
必須引数は、関数を呼び出す際に必ず指定しなければなりません。
位置引数
位置引数
位置引数は順序通りに指定することで、引数名を省略して設定できます。
可変長引数
可変長引数
可変長引数は複数回指定することができます。
作成する引数。
定義定義これらの関数や型には、関連する定義を持たせることができます。定義にアクセスするには、対象の関数や型の名前を指定した後に、ピリオド区切りで定義名を記述します。
定義
これらの関数や型には、関連する定義を持たせることができます。定義にアクセスするには、対象の関数や型の名前を指定した後に、ピリオド区切りで定義名を記述します。