このページは日本語に翻訳済みです。
datetime
日付、時刻、またはその両方を表します。
この型のコンストラクタ関数を使ってカスタム日時を指定するか、datetime.todayを使って現在の日付を取得することで作成できます。
例
#let date = datetime(
year: 2020,
month: 10,
day: 4,
)
#date.display() \
#date.display(
"y:[year repr:last_two]"
)
#let time = datetime(
hour: 18,
minute: 2,
second: 23,
)
#time.display() \
#time.display(
"h:[hour repr:12][period]"
)

DatetimeとDuration
2つのdatetimeの差を取ることで、durationを取得できます。
#let first-of-march = datetime(day: 1, month: 3, year: 2024)
#let first-of-jan = datetime(day: 1, month: 1, year: 2024)
#let distance = first-of-march - first-of-jan
#distance.hours()

datetimeとdurationを加減算することで、新しい日時(オフセットされたdatetime)を取得することもできます。
#let date = datetime(day: 1, month: 3, year: 2024)
#let two-days = duration(days: 2)
#let two-days-earlier = date - two-days
#let two-days-later = date + two-days
#date.display() \
#two-days-earlier.display() \
#two-days-later.display()

フォーマット
displayメソッドを使うことで、日時をカスタマイズして表示するフォーマットを指定できます。日時のフォーマットは、コンポーネントに修飾子を組み合わせることで指定します。
コンポーネントは、日時の中の特定の部分(例えば年や月など)を表します。そして修飾子を使うことで、そのコンポーネントをどのように表示するかを細かく設定できます。
コンポーネントを表示するには、コンポーネントの名前を角かっこで囲みます(例:[year]は年を表示します)。修飾子を追加するには、コンポーネント名の後に半角スペースを入れ、修飾子名、コロン(:)、修飾子の値を記述します(例:[month repr:short]は月名を短縮形で表示します)。
使用可能なコンポーネントと修飾子の組み合わせは以下の通りです。
year:datetimeの年を表示します。padding: 年表示のパディングはzero(ゼロ)、space(空白)、none(なし)が指定できます。repr:full(4桁表示)last_two(2桁表示)を指定できます。sign: 符号の表示をautomatic(自動)またはmandatory(常時)で指定できます。
month:datetimeの月を表示しますpadding: 月表示のパディングはzero(ゼロ)、space(空白)、none(なし)が指定できます。repr: 月を数値で表示するか(numerical)、英語の月名(long)、英語の略称(short)で表示するかを指定できます。 残念ながら、現在のところ、月名表示は英語のみです。将来的には多言語対応が予定されています。
day:datetimeの日を表示します。padding: 日表示のパディングはzero(ゼロ)、space(空白)、none(なし)が指定できます。
week_number: datetimeの週番号を表示します。padding: 週番号のパディングはzero(ゼロ)、space(空白)、none(なし)が指定できます。repr:ISO、sunday(日曜開始)、monday(月曜開始)を指定できます。ISOの場合、数字は1〜53、それ以外では0〜53で表されます。
weekday:dateの曜日を表示します。repr: 曜日名(long)、曜日名の略称(short)、日曜(sunday)、月曜(monday)のいずれかを指定できます。longとshortでは、対応する曜日名が英語で表示されます。 (月名と同様に、他言語での表示はまだサポートされていません)。sundayとmondayでは、日曜または月曜から数えた日数が数値で表示されます。one_indexed:trueまたはfalseを指定できます。これは、曜日の数値表示の際、開始日を0とするか1とするかを指定します。
hour:dateの時を表示します。padding: 時表示のパディングはzero(ゼロ)、space(空白)、none(なし)が指定できます。repr: 24時間表示(24)または12時間表示(12)を指定できます。
period: AM/PM(午前・午後)の表示です。case: 小文字(lower)、大文字(upper)を指定できます。
minute:dateの分を表示します。padding: 分表示のパディングはzero(ゼロ)、space(空白)、none(なし)が指定できます。
second:dateの秒を表示します。padding: 秒表示のパディングはzero(ゼロ)、space(空白)、none(なし)が指定できます。
全てのコンポーネントが常に使用できるとは限らない点には注意してください。例えば、datetime(year: 2023, month: 10, day: 13)のようにして新しいdatetimeを作成すると、内部的には日付のみが保持されるため、hourやminuteのようなコンポーネントは使用できません。それらは特定の時刻が指定されたdatetimeでのみ動作します。
コンストラクタ引数引数は関数への入力値です。関数名の後に括弧で囲んで指定します。
新しいdatetimeを作成。
年、月、日、時、分、秒を指定してdatetimeを作成します。
注:指定するdatetimeの要素によって、Typstが保持する形式は次の3通りのいずれかになります。
- 年、月、日だけを指定した場合、Typstは日付のみを保持します。
- 時、分、秒だけを指定した場合、Typstは時刻のみを保持します。
- 年、月、日、時、分、秒の全てを指定した場合、Typstは完全な日時を保持します。
保持形式に応じて、displayメソッドはデフォルトで異なるフォーマットを選択します。
#datetime(
year: 2012,
month: 8,
day: 3,
).display()

datetime(year:,,day:,hour:,,)->year
yeardatetimeの年。
month
monthdatetimeの月。
day
daydatetimeの日。
hour
hourdatetimeの時。
minute
minutedatetimeの分。
second
seconddatetimeの秒。
定義定義これらの関数や型には、関連する定義を持たせることができます。定義にアクセスするには、対象の関数や型の名前を指定した後に、ピリオド区切りで定義名を記述します。
today
today現在の日付を取得。
例を表示
Today's date is
#datetime.today().display().
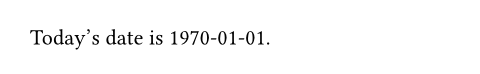
datetime.today()->display
display指定したフォーマットでdatetimeを表示します。
日付のみ、時刻のみ、または両方が指定されているかによって、デフォルトのフォーマットは異なります。
日付のみ指定されている場合は[year]-[month]-[day]になります。
時刻のみ指定されている場合は[hour]:[minute]:[second]になります。
日時の両方が指定されている場合は[year]-[month]-[day] [hour]:[minute]:[second]になります。
詳細はフォーマット構文を参照してください。
self.display()->