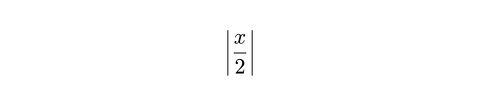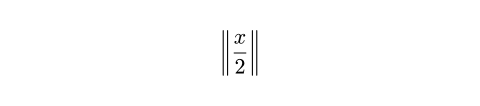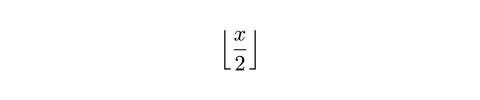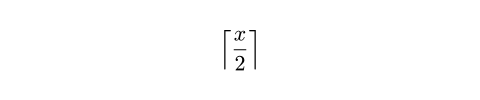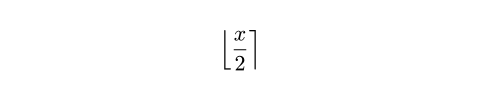部分的に翻訳済み
このページは部分的に翻訳されています。一部原文の内容が含まれています。
Left/Right
区切り文字の対応
lr関数を用いると、2つの区切り文字を対応させ、内部のコンテンツに合わせた大きさに拡大縮小できます。
これは構文的に対応が取れる区切り文字においては自動的に行われますが、lrを用いることで2つの任意の区切り文字を対応させ、その大きさを正確に制御することができます。
lr関数以外にも、Typstは、絶対値、切り捨て値、切り上げ値、ノルムを表す区切り文字ペアを生成する関数をさらにいくつか提供しています。
To prevent a delimiter from being matched by Typst, and thus auto-scaled,
escape it with a backslash. To instead disable auto-scaling completely, use
set math.lr(size: 1em).
例
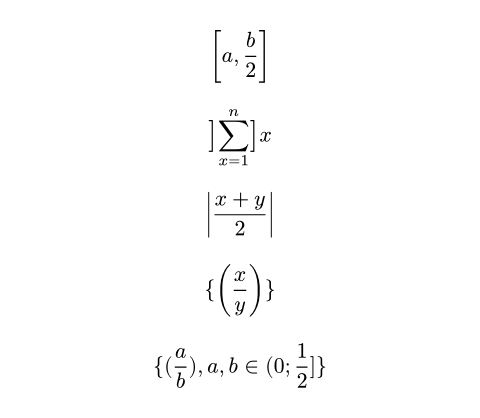
$ [a, b/2] $
$ lr(]sum_(x=1)^n], size: #50%) x $
$ abs((x + y) / 2) $
$ \{ (x / y) \} $
#set math.lr(size: 1em)
$ { (a / b), a, b in (0; 1/2] } $
Function
lr要素関数要素関数要素関数はsetルールやshowルールでカスタマイズできます。
lr要素関数
要素関数
要素関数は
setルールやshowルールでカスタマイズできます。区切り文字の拡大縮小。
対応が取れている区切り文字はデフォルトで拡大縮小しますが、これは対応が取れていない区切り文字を拡大縮小させたり、区切り文字の拡大縮小をより正確に制御するのに便利です。
math.lr(size:,)->mid要素関数要素関数要素関数はsetルールやshowルールでカスタマイズできます。
mid要素関数
要素関数
要素関数は
setルールやshowルールでカスタマイズできます。最も近くで囲んでいるlr()グループに対して、垂直方向に区切り文字を拡大縮小します。
$ { x mid(|) sum_(i=1)^n w_i|f_i (x)| < 1 } $
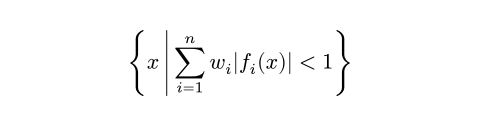
math.mid()->body
body拡大縮小させるコンテンツ。